The number of shares outstanding consists of shares held by institutions, restricted shares held by company insiders, and shares available for investors to buy and sell on the open market. A company’s outstanding shares decrease when there is a reverse stock split. A company generally embarks on a reverse split or share consolidation to bring its share price into the minimum range necessary to satisfy exchange listing requirements.
How to Calculate the Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding

The term “float” refers to the number of shares available to be traded by the public and excludes any shares held by company executives or the company’s treasury. The weighted average shares outstanding figure smooths out this variance, by simply averaging the share count across the reporting period. This is a figure calculated by the company itself; investors literally do not have the access to the data required. If a company issues new shares to the public, exercises a stock split or the employees of the company redeem the stock options, the number of outstanding shares tends to increase. On the other hand, if a company buys back the shares or practices share consolidation, the number of outstanding shares decreases.
Weighted Average of Outstanding Shares
- Treasury stock is no longer outstanding — the company itself now owns it, not an investor or employee, but it has still been issued.
- The number of shares outstanding can impact how liquid a stock is, which in turn often affects the volatility of its price.
- The cost basis refers to the original purchase price of an asset or investment for tax purposes.
- The number of outstanding shares can also change if other financial instruments are turned into shares.
- Heavy trading by closely held shareholders could also affect the stock’s weighting impact in free float capitalization indexes.
Let us understand how to calculate outstanding shares with a simple example. A food distribution company, FoodZilla Ltd has issued a total of 10,000 equity shares. Of these, 6,000 shares are floating stock i.e. held with the general public. No, float—short for floating stock or floating shares—can’t be higher than shares outstanding. It’s always a smaller figure because it only counts the number of shares available for investment and trading on financial exchanges.

Factors Influencing Outstanding Shares
The earnings per share calculation for the year would then be calculated as earnings divided by the weighted average number of shares ($200,000/150,000), which is equal to $1.33 per share. Once you know how to calculate the outstanding shares, you can use this number to calculate a number of valuation metrics, or measures of a company’s performance and future earnings potential. Outstanding shares of stock is the kind of stock issued by the company that is owned by investors, rather than by corporations themselves.
Finding Basic Shares Outstanding in Financial Statements

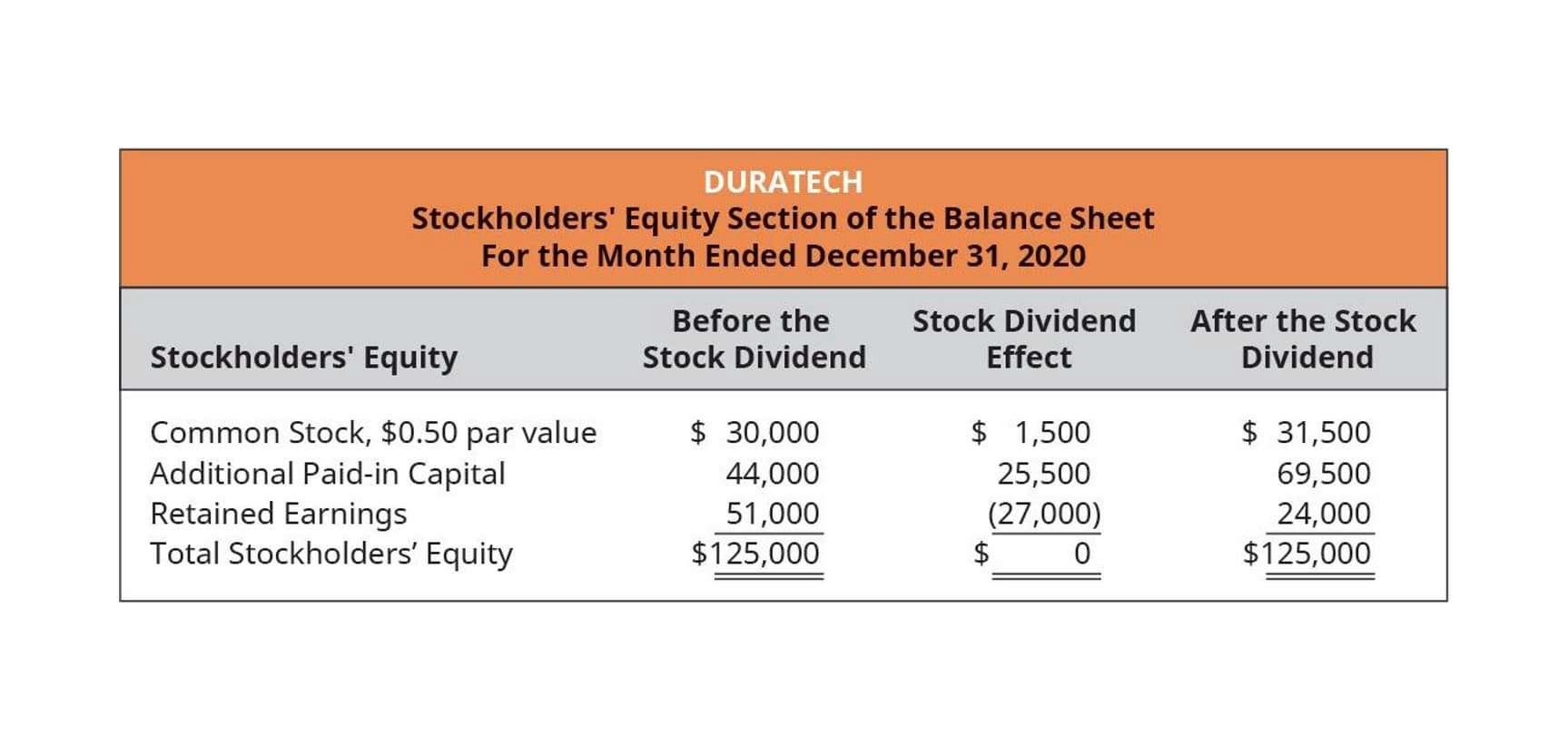
For https://www.bookstime.com/ example, when shares outstanding are going up, the ownership stake of shareholders is diluted. And when shares are bought back, investors end up owning more of the company. Shares outstanding is a financial number that represents all the shares of a company’s stock that shareholders, including investors and employees, currently own. The most up-to-date number of basic shares outstanding can be found in the latest form 10-K or 10-Q of a company. The information is available on the front page of these financial reports. Different scenarios for calculating the weighted average of outstanding shares are shown in the following examples.
- For example, the difference between the number of shares currently outstanding and the number of shares fully diluted is comparatively likely to be significant for fast-growing technology companies.
- That stock should be included in the common stock outstanding figure.
- And if these instruments are in the money, they represent current ownership of the company, even if technically the shares underlying the options, warrants or debt haven’t yet been issued.
- That’s because the vast majority of its shares are available to the general investing public.
- The number of shares outstanding consists of shares held by institutions, restricted shares held by company insiders, and shares available for investors to buy and sell on the open market.
A reverse stock split exchanges existing shares for a proportionately smaller number of new shares. Companies may do this to increase their share price, such as if they need to satisfy exchange listing requirements or want to deter short sellers. A stock split occurs when a company increases the number of its outstanding shares without changing its overall market cap or value.

But the concept of outstanding shares is a bit more complicated than it seems. The number of shares outstanding changes over time, sometimes dramatically, which can impact the calculation for a reporting period. At any how to calculate shares outstanding given point, instruments like warrants and stock options must be accounted for as well. A company’s outstanding shares may change over time because of several reasons. These include changes that take place because of stock splits and reverse stock splits. There are also considerations to a company’s outstanding shares if they’re blue chips.
Reverse Stock Split
- If you’re looking at buying stock, you can find this information is available on financial statements and through stock exchange websites.
- Using weighted average shares outstanding gives a more accurate picture of the impact of per-share measurements like earnings per share (EPS).
- The profit and loss statements in nearly every corporate earnings press release will include both basic and diluted shares outstanding.
- In certain cases, notably for companies that are aggressively issuing shares or debt, public data should be augmented with a reading of SEC filings.
- The most up-to-date number of basic shares outstanding can be found in the latest form 10-K or 10-Q of a company.
These are instruments that give the holder a right to purchase more stock from the company’s treasury. Every time one of these instruments is activated, the float and shares outstanding increase while the number of treasury stocks decreases. If all these warrants are activated, then XYZ will have to sell 100 shares from its treasury to the warrant https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc holders. While shares outstanding account for company stock that includes restricted shares and blocks of institutional shares, floating stock specifically refers to shares that are available for trading. Floating stock is calculated by taking outstanding shares and subtracting restricted shares.
The weighted average number of outstanding shares in our example would be 150,000 shares. On the balance sheet, there is a line item description that states the number of shares outstanding. Although the two both relate to the number of shares a public company has issued, they are distinct from one another. Investors use this data to calculate financial ratios, assess ownership structures, and make informed investment decisions.
